Want to be in the loop?
subscribe to
our notification
Business News
OPPORTUNITIES FOR BUSINESSES IN 5G
In the context of 5G commercialisation, businesses have the opportunity to expand and optimise their processes. Ngo Thanh Hai and Nguyen Van Anh, lawyers at LNT & Partners, discuss how these enterprises can help enhance growth efficiency.
The Ministry of Information and Communications has, as of 2024, granted licences for frequencies to deploy 5G networks to major operators like Viettel and VNPT, with the goal of achieving nationwide coverage by 2030. Viettel, the first network to successfully test commercial 5G technology in 2019, has now expanded testing to 61 provinces and cities nationwide.
VNPT and MobiFone are also vigorously advancing their 5G network development plans, installing a series of new broadcasting stations in preparation for the commercialisation phase.
Companies have prospects to expand and optimise their processes. This involves integrating this advanced technology into everyday life and business on a broad scale. This process includes developing 5G network infrastructure, licensing frequencies, and rolling out 5G services to both consumers and businesses. The aim of commercialisation is to harness the technology’s potential to drive digital transformation, enhance production efficiency, and generate economic value across various industries.
Learning from the experiences of other countries, 5G has supported smart manufacturing and supply chain optimisation in Germany and Japan. In the United States and South Korea, 5G is utilised for the development of autonomous vehicles and smart transportation systems, while in the UK and China, this technology is applied to telemedicine. E-commerce and entertainment platforms in the US, China, and South Korea also leverage 5G to enhance user experiences. Additionally, the Netherlands and Australia use 5G in agriculture to increase yields and reduce costs.
In a digital environment
The application of 5G technology will bring opportunities to many businesses. However, sectors with the potential to accelerate the digitisation process, supported by Vietnam’s current legal framework, include banking, fintech companies, e-commerce businesses, and companies that bring goods and services to online platforms.
The current development trends of credit institutions include digital transformation and the emergence of digital banks. These are banks that operate entirely in a digital environment without physical branches, thanks to advanced technological platforms such as AI, big data, cloud computing, and blockchain. Digital banking is the result of collaboration between traditional banks and fintech, offering online services through super mobile apps.
In Vietnam, the trend of fintech development is currently evident through the rise of tech startups and non-bank organisations with strong financial technological capabilities.
The Law on Credit Institutions, effective from July, introduces new provisions to accommodate emerging activities aligned with the digital transformation trend. This includes the authorisation of a testing mechanism for fintech innovations in banking, online lending, and electronic transactions.
To facilitate the implementation of this testing mechanism, the State Bank of Vietnam is developing a draft on a controlled testing framework in the banking sector, focusing on fintech companies and solutions applied to banking operations. To prioritise online transactions, the government has also enacted Decree No.52/2024/ND-CP, which outlines regulations for non-cash payments. This decree includes additional provisions regarding cryptocurrencies, international payments, and e-wallets and prepaid cards applicable to credit institutions.
The use of 5G technology is pivotal in supporting digital transformation goals and advancing related banking, as highlighted by current development trends in credit institutions. With its superior data transmission speeds and low latency, 5G enables such banks to deliver online services more swiftly and efficiently, particularly in real-time transactions such as electronic payments and transfers.
Furthermore, 5G enhances connectivity and integration with advanced technology platforms like AI, big data, and blockchain, allowing digital banks to offer intelligent, personalised financial services and strengthen transaction security.
Meanwhile, in the relationship between traders owning e-commerce platforms and customers, traders are required to ensure the security of payment activities in accordance with Article 74 of Decree 52. This includes encrypting information and using security protocols to protect data from exposure during transmission, maintaining an information system that ensures continuous online connectivity 24/7, among other measures.
Assessing the risks
In the contractual relationship between buyers and sellers, electronic contracts with digital signatures are increasingly reinforced by Decree No.48/2024/ND-CP of this year and the development of smart contracts utilising blockchain technology. In this context, 5G technology’s rapid data transmission speeds and low latency enhance the efficiency of processing and verifying contracts, including those involving e-signatures and smart contracts on blockchain platforms.
Regarding interactions with payment intermediaries, Article 75 of Decree 52 stipulates that intermediaries must ensure data storage for each payment transaction and share joint responsibility with merchants for information management. Given the growing volume of online transactions, 5G technology enables payment intermediaries to store and access transaction data more efficiently, providing better security for customer information.
There is currently no legal framework regulating the application of fintech. To accelerate the adoption of digital banking and fintech within credit institutions and relevant companies, it is essential that the draft decree on controlled testing mechanisms in banking be implemented without delay.
Secondly, concerning the legal value of smart contracts utilising blockchain technology, there is currently no legal framework that formally recognises their legal standing. Although Article 385 of the Civil Code 2015 and Article 34 of Law on Electronic Transactions 2023 suggest that smart contracts possess the full legal nature of civil and electronic contracts, the law still lacks explicit recognition of their legal value.
Furthermore, concerning cybersecurity in transaction activities and customer data storage, this represents a significant risk associated with the adoption of new technologies. Currently, the Cybersecurity Law provides the legal foundation for mechanisms to protect information security on the internet. Decree No.13/2023/ND-CP from 2023 outlines rules and reporting requirements for personal data protection to cybersecurity agencies. However, there remains a lack of a regulatory framework for penalties related to personal data protection. Therefore, a penalty decree should be issued promptly to encourage businesses to enhance their awareness of information security while implementing advanced tech.
In the short term, prioritising investment in technological infrastructure, bolstering security measures, and optimising electronic transaction processes is essential. As legal mechanisms become fully established and enforced, businesses should engage closely with regulatory bodies to ensure the efficient and secure implementation of 5G in their operations.
Source: VIR
Related News

PRACTICAL CONSTRUCTION WORK
At Phuc Vuong, we do not focus on talking about our capabilities. Instead, every project currently under construction serves as the clearest and most direct proof. From site preparation, piling works, and foundation construction to structural works and major items, our technical team remains closely involved on site, monitoring every detail.
INTERNATIONAL ARRIVALS TO PHU QUOC AT RECORD HIGH
On January 17, Phu Quoc International Airport handled 47 international flights in a single day, the highest level since the airport began operations. Earlier, on January 3, the airport had already set a new record with 46 international flights in one day. Notably, the surge was not confined to a few peak days. International arrivals were maintained at a high level throughout January, pointing to a more sustained and stable expansion of the international travel market to the island.

VIETNAM PUTS SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AT CENTER OF 2026 GROWTH STRATEGY
Vietnam will make science and technology, innovation and digital transformation the core drivers of economic growth in 2026, under a Government resolution guiding this year’s socio-economic development and budget implementation. The direction is set out in Resolution No. 01 on key tasks and solutions for 2026, reported the Government news website (baochinhphu.vn).

VIETNAM ECONOMIC NEWS INSIGHT & RECAP - DECEMBER 2025
Vietnam closed 2025 with an impressive economic performance, exceeding initial targets and demonstrating the resilience of its growth model. Full-year GDP expanded by 8.02% supported by a combination of government-led stimulus, stable domestic production and consumption, and continued strength in key export sectors amid ongoing external uncertainties.
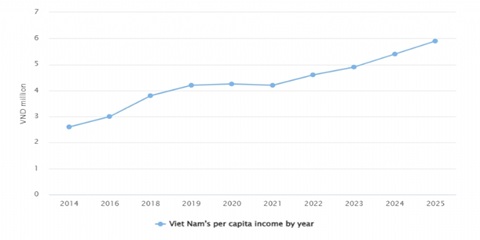
PER CAPITA INCOME CLIMBS 9.3% IN 2025
Average per capita income in 2025 was estimated at VND5.9 million (approximately US$225) per month, marking a 9.3 percent increase from 2024, according to preliminary findings of the Household Living Standards Survey 2025 conducted by the National Statistics Office (NSO). Part of the income growth stemmed from State payments to public officials and employees who retired or resigned under the restructuring of the political system's organizational apparatus.

INDUSTRY AND TRADE SECTOR MAINTAINING GROWTH MOMENTUM, FORGING SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
In 2025, Hai Phong City benefited from significant opportunities created by an expanded development space following administrative consolidation, while also facing challenges in maintaining stable and efficient administrative operations and sustaining strong economic growth amid ongoing global volatility. Within this context, the industry and trade sector continued to serve as an important driving force for the city’s overall economic growth.
























